Investments by insurers under Solvency II are crucial for financial stability. This framework mandates specific strategies, impacting capital requirements and performance. Understanding these intricacies is vital for navigating the evolving landscape of insurance investment.
Solvency II’s impact on investment strategies extends across various aspects, from permissible investments to risk management methodologies. This analysis explores the key components, challenges, and opportunities for insurers adapting to this regulatory environment.
Overview of Solvency II
Solvency II, a cornerstone of European insurance regulation, ascends as a majestic edifice, meticulously crafted to fortify the resilience of the insurance industry. Its architecture, encompassing intricate calculations and stringent guidelines, aims to bolster the financial stability of insurers, safeguarding policyholders and the broader economic landscape.This framework, designed with a profound understanding of the complexities inherent in the insurance sector, meticulously regulates the capital adequacy and risk management practices of insurers.
Its comprehensive nature ensures a level playing field across the continent, promoting trust and fostering a robust insurance environment.
Solvency II Framework
Solvency II establishes a robust framework for assessing the solvency of insurance undertakings. It moves beyond rudimentary capital adequacy assessments, embracing a holistic approach that encompasses all facets of risk. This intricate framework ensures that insurers possess sufficient capital to meet their obligations, thereby safeguarding the interests of policyholders.
Key Objectives and Principles
The core objectives of Solvency II are multifaceted, focusing on enhancing the stability and security of the insurance sector. These objectives are realized through a set of guiding principles that underpin the framework’s application. Central to these principles is the commitment to a harmonized regulatory environment, fostering a unified approach across Europe.
- Promoting Financial Stability: Solvency II seeks to minimize the systemic risk within the insurance sector by enforcing robust capital requirements. This translates to a stronger and more resilient insurance market, capable of weathering economic storms. Examples of such storms include the 2008 financial crisis and the subsequent economic downturns, demonstrating the crucial need for a robust framework like Solvency II.
- Protecting Policyholders: The framework directly benefits policyholders by ensuring insurers possess sufficient capital to meet their obligations. This principle ensures the continuation of benefits and services, fostering public trust in the insurance industry. The stability and reliability of the insurance industry underpin the confidence of policyholders.
- Harmonizing European Regulations: Solvency II harmonizes insurance regulations across European Union member states, eliminating the inconsistencies and complexities associated with diverse national frameworks. This creates a single, unified market, boosting efficiency and facilitating cross-border operations.
Regulatory Context for Insurers
Solvency II’s regulatory context profoundly impacts the operations of insurance companies. It necessitates a significant shift in how insurers approach risk management, capital adequacy, and reporting obligations. This new paradigm fosters transparency and accountability, thereby strengthening the regulatory oversight of insurers.
- Capital Adequacy Requirements: Insurers are obligated to maintain capital reserves that sufficiently cover potential losses, reflecting the various risks inherent in their operations. This approach ensures a buffer against unexpected events and financial shocks.
- Risk Management: Solvency II compels insurers to implement comprehensive risk management strategies. This includes the identification, assessment, and mitigation of diverse risks, encompassing market, credit, and operational risks.
- Reporting Obligations: Insurers must comply with stringent reporting obligations to regulatory authorities. This transparency allows for continuous monitoring and oversight of insurer solvency, providing regulators with valuable insights.
Historical Context
The implementation of Solvency II is deeply rooted in the historical context of European insurance regulation. It emerged from a recognition of the need for a unified approach to solvency standards across the European Union. This recognition arose from the experiences of past financial crises, which highlighted the vulnerabilities of fragmented and inconsistent regulatory environments.
- Evolution of European Insurance Regulation: Solvency II is a logical evolution of European insurance regulation, building upon existing frameworks and incorporating lessons learned from past events. The framework aims to avoid the repetition of past regulatory failures.
Types of Insurance Activities Covered
Solvency II encompasses a wide spectrum of insurance activities, covering various lines of business. It extends to all types of insurance contracts and undertakings operating within the European Union. This comprehensive coverage underscores the framework’s breadth and depth.
- Life Insurance: Solvency II’s provisions encompass life insurance products, including traditional life insurance, pensions, and annuities.
- Non-Life Insurance: It also includes non-life insurance, encompassing motor, property, and casualty insurance.
- Reinsurance: Reinsurance activities are also included within the purview of Solvency II, recognizing the crucial role of reinsurance in managing risks for primary insurers.
Investment Strategies under Solvency II: Investments By Insurers Under Solvency Ii
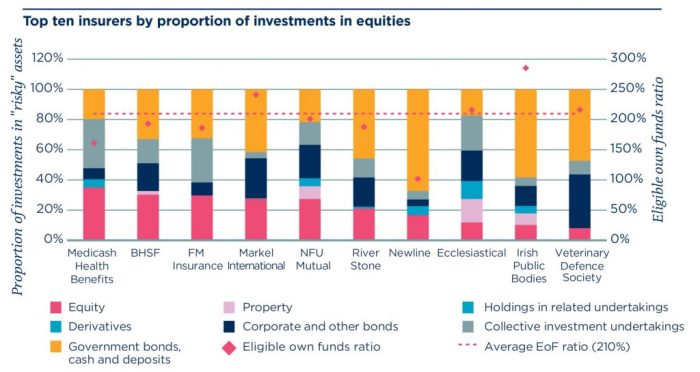
Insurers, navigators of the financial seas, now chart their courses under Solvency II’s watchful eye. This regulatory framework, a symphony of prudence and precision, dictates the very investments that shape their future. The music of investment strategy, once free-flowing, now plays within a carefully orchestrated score.Investment strategies under Solvency II are no longer a matter of personal preference, but a meticulously calculated dance between risk and reward.
The framework’s intricate design compels insurers to prioritize capital adequacy, and to carefully consider the implications of each investment choice. This calculated approach, while demanding, ultimately safeguards the stability of the insurance industry.
Key Investment Considerations for Insurers
Insurers must consider a multitude of factors when designing their investment strategies. These factors include the nature of their liabilities, the specific risks inherent in different asset classes, and the overall economic climate. This necessitates a deep understanding of market dynamics and the potential for unforeseen events.
- Liability Matching: A crucial consideration is the alignment between the insurer’s investment portfolio and the timing and nature of its liabilities. This ensures the portfolio can effectively meet its obligations as they mature, safeguarding against potential mismatches and financial stress.
- Risk Appetite and Tolerance: Insurers must clearly define their risk appetite and tolerance levels. This translates into selecting investments that align with their comfort zones, ensuring a balance between potential returns and acceptable risk.
- Regulatory Requirements: Solvency II mandates specific requirements regarding the calculation of solvency capital requirements. Insurers must meticulously track their investments to ensure they satisfy these requirements.
Permitted Investment Strategies
Solvency II permits a wide range of investment strategies, recognizing the diversity of insurers and their individual needs. These strategies encompass various asset classes, each with its own set of inherent risks and rewards.
- Fixed Income Investments: Bonds, notes, and other fixed-income instruments offer predictable returns and relative stability. Their suitability depends on the insurer’s specific liability profile and risk tolerance.
- Equities: Investments in stocks provide the potential for higher returns but also carry greater volatility. Insurers must carefully assess the market outlook and their ability to withstand potential market downturns.
- Real Estate: Real estate investments can offer diversification and potentially stable returns. However, factors like market conditions and local regulations must be carefully considered.
- Alternative Investments: These include private equity, hedge funds, and other less-conventional assets. These investments can offer potentially higher returns but carry significant complexity and risk.
Comparison of Investment Strategies
Different investment strategies offer varying degrees of risk and return potential. Insurers must meticulously evaluate the characteristics of each strategy, considering their own specific needs and circumstances.
| Investment Strategy | Risk | Return Potential | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Income | Low | Moderate | Suitable for insurers with a conservative approach |
| Equities | High | High | Suitable for insurers with a higher risk tolerance and longer investment horizons |
| Real Estate | Moderate | Moderate | Suitable for insurers seeking diversification and potential inflation hedge |
| Alternative Investments | High | High | Suitable for insurers seeking diversification and potentially high returns but with substantial due diligence required |
Impact on Diversification Strategies
Solvency II emphasizes the importance of diversification, demanding insurers to spread their investments across various asset classes. This reduces the impact of adverse events in specific sectors or markets. This strategy is pivotal for insurers’ long-term financial stability.
- Geographic Diversification: Spreading investments across different geographic regions can mitigate risks associated with local economic fluctuations.
- Asset Class Diversification: Investing in a mix of asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, minimizes the impact of market downturns in any one sector.
Risk Management Implications
Effective risk management is paramount under Solvency II. Insurers must develop robust risk management frameworks to monitor and control the risks associated with their investment strategies. This includes scenario analysis and stress testing to anticipate potential adverse outcomes.
Risk management is not a one-time event but a continuous process requiring regular review and adaptation.
Capital Requirements and Investments
Insurers, guardians of financial futures, navigate a labyrinth of capital requirements under Solvency II. These stringent regulations, woven from threads of risk assessment and financial prudence, dictate the tapestry of investment choices. Understanding the intricate dance between capital and investments is paramount for a successful insurance enterprise.
Relationship Between Capital Requirements and Investment Choices
Solvency II establishes a direct correlation between capital requirements and investment strategies. Higher risk investments, like those in emerging markets, often necessitate more capital to absorb potential losses. Conversely, lower-risk investments, such as government bonds, may demand less capital. This principle, akin to a carefully calibrated scale, ensures insurers maintain sufficient reserves to meet obligations, fostering financial stability.
Factors Influencing Capital Requirements for Investments
Numerous factors influence the capital needed for various investment types. Market volatility, creditworthiness of borrowers, and the inherent risk profile of the investment are key determinants. The insurer’s risk appetite and the diversification of the portfolio also play a pivotal role. These variables, like the stars in a celestial dance, combine to define the capital cushion required for the insurer’s operations.
Impact of Different Investment Types on Solvency Capital Requirement
Different investment types have varying impacts on the solvency capital requirement (SCR). Equity investments, characterized by their potential for substantial gains, often carry higher SCRs. Conversely, debt investments, typically offering more predictable returns, usually have lower SCRs. This nuanced relationship highlights the necessity of carefully balancing risk and return within the portfolio.
Calculation of Capital Requirements for Investment Portfolios
Calculating SCRs for specific investment portfolios involves a complex process, using formulas and methodologies defined by Solvency II. The process begins with assessing the risk associated with each investment within the portfolio. These risk assessments are often based on standardized models, such as the Internal Ratings-Based (IRB) approach. The final capital requirement is a sum of the individual SCRs for each investment, reflecting the collective risk profile of the portfolio.
SCR = f(Risk Parameters, Investment Types)
Illustrative Impact on Capital Adequacy Ratios
| Investment Type | Estimated Impact on Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Government Bonds | Low | Generally low-risk, predictable returns lead to lower capital requirements. |
| Corporate Bonds | Moderate | Higher risk compared to government bonds, requiring a corresponding increase in capital. |
| Equities | High | Significant potential for gain, but also for loss, demanding higher capital reserves to absorb potential downturns. |
| Real Estate | Moderate to High | Risk depends on the specific type of real estate investment and market conditions. |
The table above illustrates the potential impact of different investment choices on an insurer’s CAR. The CAR, a critical metric reflecting the insurer’s ability to meet its obligations, is directly influenced by the risk profile of the investments held in the portfolio. For example, an insurer heavily invested in equities might experience a lower CAR compared to one primarily investing in government bonds.
A well-diversified portfolio, strategically balancing risk and return, is crucial to maintain an acceptable CAR.
Impact of Solvency II on Investment Performance
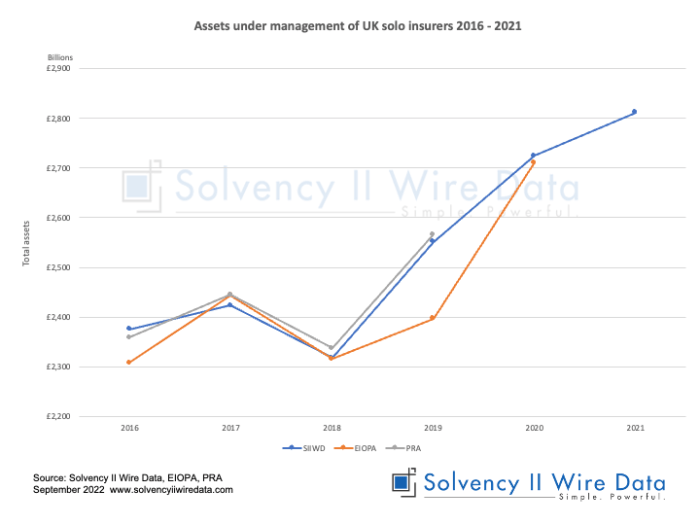
Solvency II, a landmark European Union directive, has reshaped the landscape of insurance investment strategies. Its intricate framework, designed to enhance the financial stability of insurers, has had profound and multifaceted effects on their investment returns. The regulatory changes have ushered in a new era of calculated risk-taking and prudent portfolio management.The Solvency II regime introduced a more rigorous approach to capital adequacy and risk assessment.
Insurers’ investments under Solvency II regulations are a complex area, requiring careful consideration of risk and return. A key aspect is the strategic allocation of capital, and this often involves diversification across various asset classes. Considering the popularity of casual dining options, one might consider the diverse menu choices at Johnnie’s Pizza and Wings, johnnies pizza and wings menu , as a microcosm of the diversified portfolio approach.
Ultimately, the prudent investment strategies of insurers under Solvency II need to align with long-term financial goals and regulatory requirements.
This shift necessitates a more sophisticated understanding of investment performance, demanding that insurers meticulously evaluate and manage the risks associated with each investment. This approach, while potentially impacting returns in the short term, aims to secure long-term stability and investor confidence.
Effect on Investment Returns
The implementation of Solvency II has exerted a significant influence on investment returns for insurers. The heightened capital requirements often lead to a more conservative investment approach. Insurers may allocate a greater portion of their assets to safer, less volatile instruments to ensure compliance with the new regulations. This, in turn, can potentially affect the rate of return compared to pre-Solvency II strategies.
The effect varies based on the specific investment portfolio and the insurer’s risk appetite.
Comparative Analysis of Performance Trends, Investments by insurers under solvency ii
Analyzing investment performance trends before and after Solvency II necessitates careful consideration of various factors, such as market conditions and individual insurer strategies. Historical data reveals that, in certain periods following the implementation of Solvency II, some insurers experienced a slight dip in returns, particularly in the short term. However, this is often countered by a greater degree of long-term stability.
The precise impact varies across different asset classes and geographic markets.
Key Metrics for Measuring the Impact
Several key metrics are crucial for assessing the impact of Solvency II on insurers’ investment performance. These include return on assets (ROA), return on equity (ROE), Sharpe ratio, and the overall risk-adjusted return. Monitoring these metrics before, during, and after Solvency II implementation allows for a comprehensive understanding of the regulatory changes’ effect on profitability and risk management.
A detailed analysis of these metrics, across various insurers and asset classes, offers invaluable insights.
Challenges and Opportunities for Insurers
The shift towards a more stringent regulatory environment, imposed by Solvency II, presents both challenges and opportunities for insurers. The increased capital requirements may limit investment opportunities, especially in riskier assets, thereby potentially impacting the overall return. However, the emphasis on risk management and diversification could lead to more stable and sustainable investment strategies.
Adaptations in Investment Strategies
Insurers have adopted various strategies to navigate the Solvency II landscape. Some have diversified their investment portfolios to reduce risk, allocating a larger percentage to low-risk assets like government bonds. Others have refined their risk models to more accurately assess the risks associated with their investments, leading to a more sophisticated approach to portfolio management. Examples include the implementation of stress testing to evaluate the resilience of their portfolios under adverse market conditions.
Moreover, there’s a noticeable trend towards greater transparency and disclosure regarding investment strategies and performance, in compliance with the new regulations. These adaptations are essential to maintain long-term financial stability and compliance.
Recent Developments and Trends
The intricate tapestry of Solvency II, woven with threads of regulatory oversight and investment strategy, has seen recent embellishments and shifts. Insurers navigate a landscape of evolving regulations, striving to maintain financial stability while capitalizing on burgeoning investment opportunities. This dynamic environment demands keen awareness and adaptability, driving innovation and a pursuit of optimal investment practices.The Solvency II framework, a cornerstone of insurance regulation, continues to evolve with adjustments to investment guidelines.
These updates aim to ensure insurers maintain a robust capital base while fostering responsible investment practices. The spirit of this evolution is to strengthen the resilience of the insurance sector against economic fluctuations, safeguarding policyholders’ interests.
Regulatory Updates and Interpretations
Recent regulatory updates, often disseminated through official pronouncements and circulars, have clarified certain aspects of Solvency II’s investment provisions. These clarifications address potential ambiguities and provide a more precise framework for insurers’ investment decisions. This has resulted in a clearer understanding of how to assess risks associated with alternative investments, like private equity or real estate, within the Solvency II framework.
Moreover, there’s been an increased emphasis on the importance of stress testing investment portfolios to anticipate potential economic downturns.
Current Trends and Challenges
Investment management for insurers under Solvency II is characterized by a delicate balance between regulatory compliance and maximizing returns. Insurers face the challenge of aligning investment strategies with Solvency II’s capital requirements while simultaneously generating attractive returns. This often necessitates diversification, exploring alternative asset classes, and adapting to market volatility. Furthermore, the growing demand for sustainable and responsible investments has become a significant trend, influencing investment portfolios.
Innovative Investment Approaches
Insurers are embracing innovative approaches to meet the requirements of Solvency II and potentially improve returns. One example is the increasing use of sophisticated quantitative models to assess and manage investment risks. These models enable insurers to develop more tailored and precise strategies, enhancing risk-adjusted returns. Furthermore, collaborations with specialized investment managers and fintech companies are emerging as strategic partnerships to unlock access to niche investment opportunities.
Industry Best Practices
Developing and maintaining robust investment governance frameworks is a key industry best practice. These frameworks establish clear guidelines and responsibilities for investment decisions, ensuring alignment with Solvency II regulations and promoting transparency. Insurers are increasingly emphasizing the importance of robust due diligence processes for all investment opportunities. This diligence ensures that investments meet the standards of Solvency II and align with the insurer’s risk appetite.
Key Conferences and Publications
- Insurers and financial institutions regularly participate in conferences like the “European Insurance and Pension Conference” and various industry-specific seminars to stay updated on Solvency II developments and share best practices.
- Specialized publications, such as “The Insurance Journal” and “Insurance Europe,” often feature articles and analysis on Solvency II’s implications for investment strategies.
Cross-border Investments and Solvency II
Across the vast expanse of global finance, Solvency II stands as a beacon, guiding insurers in their investment journeys. Navigating the intricate pathways of cross-border investments, however, requires a nuanced understanding of this regulatory framework. This section delves into the intricacies of Solvency II’s impact on insurers’ international investment activities.Insurers, seeking to diversify their portfolios and capture global market opportunities, often engage in cross-border investments.
Solvency II, however, imposes specific requirements and considerations on these activities. It necessitates a meticulous assessment of the risks associated with international investments, ensuring a robust risk management framework is in place to safeguard the solvency of the insurance entity.
Insurer investments under Solvency II regulations are a complex area, with various factors influencing strategies. A prime example of a company navigating these regulations is New York Life Insurance, with offices in Queens, offering a range of financial products and services. new york life insurance queens. Ultimately, these investment decisions significantly impact the financial health and stability of insurance companies operating under Solvency II.
Impact on Investment Activities
Solvency II mandates a comprehensive risk assessment of each investment, regardless of its location. This includes considering the creditworthiness of foreign counterparties, political and economic stability of the host country, and currency fluctuations. Insurers must meticulously document their investment strategies and the rationale behind their choices to demonstrate compliance with the regulatory framework. This rigorous approach helps to prevent unforeseen losses and ensure the stability of the insurance enterprise.
Challenges in Cross-Border Investments
Numerous challenges emerge when navigating the intricacies of cross-border investments under Solvency II. Different regulatory landscapes across nations present complexities in aligning investment strategies with the requirements of each jurisdiction. Ensuring the consistent application of accounting standards and reporting procedures across borders demands considerable effort. Additionally, the potential for currency fluctuations adds a layer of volatility to investment returns, necessitating robust hedging strategies to mitigate the impact.
Opportunities for Insurers
Cross-border investments, despite the challenges, provide considerable opportunities for insurers. Diversification of investment portfolios through access to international markets can potentially enhance returns and mitigate risks. By tapping into emerging markets, insurers can unlock opportunities for long-term growth and capital appreciation. This diversification is critical for navigating the volatile global economic landscape.
Regulatory Harmonization Efforts
Efforts to harmonize regulatory frameworks concerning investments across borders are ongoing. These efforts aim to create a more unified and predictable environment for insurers operating in multiple jurisdictions. The shared goal is to reduce inconsistencies in standards and procedures, thereby streamlining investment processes and facilitating a more transparent and fair marketplace. This ongoing harmonization is essential for promoting a level playing field for insurers globally.
Comparison with Other Jurisdictions
Comparing Solvency II’s requirements with those of other jurisdictions reveals a complex tapestry of similarities and differences. While many jurisdictions share a commitment to financial stability, the specifics of their regulatory frameworks often vary significantly. The level of detail in capital requirements, reporting standards, and risk management protocols can differ greatly, necessitating a tailored approach for insurers operating in multiple markets.
Understanding these nuances is essential for navigating the diverse regulatory landscape effectively.
Examples of Successful Strategies
Several successful examples demonstrate how insurers have effectively navigated cross-border investments under Solvency II. These include diversifying portfolios by investing in high-yield bonds from emerging markets, while simultaneously employing sophisticated hedging strategies to mitigate currency risk. Another strategy involves forming strategic partnerships with local investment managers to leverage their expertise in navigating the unique investment landscapes of specific regions.
These strategies showcase how insurers can effectively balance risk and reward in the global marketplace.
Final Summary
In conclusion, navigating investments under Solvency II requires a nuanced understanding of capital requirements, risk management, and regulatory developments. Insurers must adapt their strategies to meet the framework’s demands while maximizing returns. This detailed examination provides valuable insights for navigating the complexities of this evolving landscape.
Quick FAQs
What are the common investment types permitted under Solvency II?
Solvency II permits investments in a range of assets, including government bonds, corporate bonds, equities, and real estate. Specific asset classes and their allocations are subject to capital requirements and risk assessments.
How does Solvency II affect cross-border investments?
Solvency II introduces specific requirements for cross-border investments, impacting capital adequacy and risk management procedures for insurers operating internationally. Harmonization efforts aim to streamline these procedures across different jurisdictions.
What are the key metrics for assessing the impact of Solvency II on investment performance?
Key metrics include return on investment, capital adequacy ratio, and risk-adjusted returns. These metrics help assess the efficiency and effectiveness of investment strategies in light of Solvency II requirements.
What are the potential challenges insurers face adapting to Solvency II requirements?
Adapting to Solvency II often presents challenges related to compliance, increased administrative burden, and potential changes in investment returns. Careful planning and strategic adaptation are crucial for mitigating these issues.
